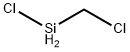CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Methyldichlorosilane appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor. Flash point: -26 °F; Boiling point: 41 °C (106 °F). Vapors heavier than air. Vapor and liquid may cause burns. Denser than water and decomposed by water to form hydrochloric acid, a corrosive material. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | ACRID ODOR |
| Boiling Point | 106.7 °F at 760 mmHg (USCG, 1999) |
| Melting Point | -135 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Flash Point | -14 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Solubility | Sol in benzene, ether, heptane |
| Density | 1.11 at 77 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 3.97 (AIR= 1) |
| Vapor Pressure | 429.0 [mmHg] |
| LogP | log Kow = 1.7 at 25 °C |
| Autoignition Temperature | greater than 600 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition | Toxic hydrogen chloride and phosgene gases may be formed. |
| Heat of Combustion | -4,700 BTU/LB |
| Heat of Vaporization | 106 BTU/LB |
| Refractive Index | INDEX OF REFRACTION: 1.3983 @ 20 °C/D |
| Other Experimental Properties | RELEASES HYDROGEN IN AN ALKALINE MIXTURE |
| Chemical Classes | Toxic Gases & Vapors -> Chlorosilanes |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 114.02 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 112.9381070 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 112.9381070 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 13.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Methyldichlorosilane appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor. Flash point: -26 °F; Boiling point: 41 °C (106 °F). Vapors heavier than air. Vapor and liquid may cause burns. Denser than water and decomposed by water to form hydrochloric acid, a corrosive material.