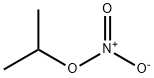
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Isopropyl nitrate appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. May spontaneously decompose and explode under prolonged exposure to fire or heat. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. |
|---|---|
| Vapor Pressure | 34.1 [mmHg] |
| Kovats Retention Index | 663.8 664 664 693 |
| Chemical Classes | Nitrogen Compounds -> Nitrates and Nitrites |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P220:Keep/Store away from clothing/…/combustible materials. P221:Take any precaution to avoid mixing with combustibles/… P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 105.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 105.042593085 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 105.042593085 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 55 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 65.1 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Isopropyl nitrate appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. May spontaneously decompose and explode under prolonged exposure to fire or heat. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.