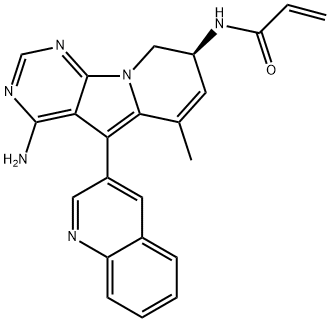
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 396.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 396.16985928 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 396.16985928 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 98.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 710 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Zipalertinib is an orally available selective inhibitor of a broad spectrum of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, including EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations (EGFR Ex20ins; Ex20ins mutations), with potential antineoplastic activity. CLN-081 is also active against other EGFR mutations including exon 19 deletions (exon19del), L858R, and T790M, as well as the less common G719X, L861Q and S768I mutations. Upon administration, zipalertinib specifically and covalently binds to and inhibits a variety of EGFR mutations, with particularly high selectivity against EGFR Ex20ins, which prevents EGFR mutant-mediated signaling and leads to cell death in EGFR mutant-expressing tumor cells. Compared to some other EGFR inhibitors, CLN-081 may have therapeutic benefits in tumors with EGFR Ex20ins, as most EGFR mutant-selective inhibitors are not active against EGFR Ex20ins. This agent shows minimal activity against wild-type EGFR (wt EGFR), and does not cause dose-limiting toxicities that occur during the use of non-selective EGFR inhibitors, which also inhibit wt EGFR. EGFR, a receptor tyrosine kinase mutated in many tumor cell types, plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation and tumor vascularization.