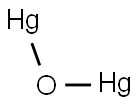CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Black solid; [Hawley] Brown to black odorless powder; [MSDSonline] |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Black or brownish-black powder |
| Melting Point | 100 °C (decomposes to elemental mercury) |
| Solubility | Insol in water; sol in nitric acid |
| Density | 9.8 |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition ... emits highly toxic fumes of /mercury/. |
| Surface Tension | 75.6 DYNES/CU M |
| Other Experimental Properties | Hydrochloric acid converts it into calomel. |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Mercury Compounds, Inorganic |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 417.18 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 417.933885 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 419.93620 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 9.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Mercury(I) oxide is an oxide of mercury. Mercury is a heavy, silvery d-block metal and one of six elements that are liquid at or near room temperature and pressure. It is a naturally occuring substance, and combines with other elements such as chlorine, sulfur, or oxygen to form inorganic mercury compounds (salts). Mercury also combines with carbon to make organic mercury compounds. (L1)