150-13-0
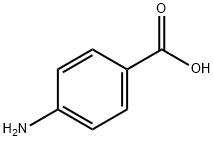
Product Name:
4-Aminobenzoic acid
Formula:
C7H7NO2
Synonyms:
4-Aminobenzoic acid;PABA;para-Aminobenzoic acid;Vitamin Bx;Vitamin H1
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | P-aminobenzoic acid appears as colorless crystals that discolor on exposure to light and air. (NTP, 1992) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Monoclinic prisms from dilute alcohol |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting Point | 370 to 372 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility | >20.6 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4) |
| Density | 1.37 (NTP, 1992) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.000278 [mmHg] |
| LogP | 0.83 |
| LogS | -0.4 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Chemical stability: Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
| pH | pH (0.5% solution): 3.5 |
| Ionization Efficiency | Negative |
| Dissociation Constants | 4.874 |
| Collision Cross Section | 131 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine] |
| Kovats Retention Index | 1547 |
| Other Experimental Properties | May turn slightly yellow on prolonged exposure to light and air |
| Chemical Classes | Other Uses -> Sunscreens |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Warning |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 137.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 137.047678466 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 137.047678466 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 128 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
P-aminobenzoic acid(PABA) appears as colorless crystals that discolor on exposure to light and air. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite, a plant metabolite and an allergen. It is functionally related to a benzoic acid. It is a conjugate base of a 4-carboxyanilinium. P-aminobenzoic acid occurs naturally in the body. It is also found in several foods including grains, eggs, milk, and meat. PABA is taken for a disease that causes curved, painful erections (Peyronie disease), a rare autoimmune disorder that causes skinblisters (pemphigus), hardening of skin and connective tissue (scleroderma), and many other conditions.
