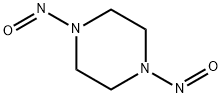
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Pale yellow solid; [HSDB] |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | PALE YELLOW PLATES FROM WATER |
| Melting Point | 158 °C |
| Solubility | SLIGHTLY SOL IN WATER, ACETONE; VERY SOL IN HOT ALCOHOL |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.00019 [mmHg] |
| LogP | -0.85 |
| Chemical Classes | Nitrogen Compounds -> Nitrosamines |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 144.13 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 144.06472551 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 144.06472551 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 65.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 115 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Carcinogen is any chemical, biological or physical agents that increase the risk of neoplasms in humans or animals. Carcinogens include natural or synthesized compounds, certain viruses, and various sources of radiation. A carcinogen may directly alter the genetic material of cells (genotoxic), thereby initiating or promoting the process of malignant transformation; it also may induce cancers by mechanisms that do not involve a direct alteration of cellular genetic material (non-genotoxic). (NCI04)