CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White crystals from CH2Cl2/ether |
| Melting Point | 99-100 °C (decomposes) |
| Vapor Pressure | 2.2X10-15 mm Hg at 25 °C /Estimated/ |
| LogP | 0.6 |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant: 1.2X10-17 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C /Estimated/ |
| Other Experimental Properties | White crystals from ether, mp 140-141 °C (decomposes) /Sodium salt/ |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 359.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 359.13036271 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 359.13036271 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 96.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 440 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
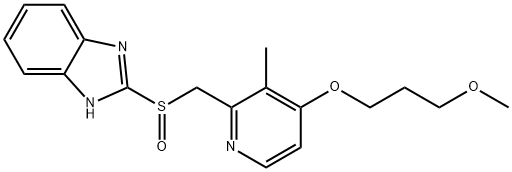
Rabeprazole is a member of benzimidazoles, a sulfoxide and a member of pyridines. It has a role as an EC 3.6.3.10 (H(+)/K(+)-exchanging ATPase) inhibitor and an anti-ulcer drug. It is a conjugate acid of a rabeprazole(1-).