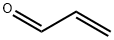CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Acrolein, stabilized appears as a colorless to yellow volatile liquid with a disagreeable choking odor. Flash point below 0 °F. Initially irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes. Very toxic by inhalation. Less dense than water (7.0 lb / gal). Vapors heavier than air. Used to make other chemicals, plastics, and as a herbicide. Rate of onset: Immediate Persistence: Minutes to hour Odor threshold: 1 ppm Source/use/other hazard: Herbicide; tox and corrosive fumes. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless or yellowish liquid |
| Odor | Extremely sharp; extremely acrid, pungent, burnt sweet; hot fat |
| Boiling Point | 126 °F at 760 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Melting Point | -126 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Flash Point | -15 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | greater than or equal to 100 mg/mL at 70 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 0.8389 to 0.8621 at 32 to 68 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Vapor Density | 1.94 (EPA, 1998) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 135.71 to 210 mmHg at 50 to 68 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP | log Kow = -0.01 |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant = 1.22X10-4 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
| Autoignition Temperature | 453 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition | Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides. |
| Viscosity | 0.35 cP at 20 °C |
| Corrosivity | Non-corrosive to iron & steel at room temperature |
| Heat of Combustion | -12,500 BTU/lb = -6,950 cal/g = -290X10+5 J/kg |
| Heat of Vaporization | 216 BTU/lb = 120 cal/g = 5.02X10+5 J/kg |
| pH | pH 6.0 (max), a 10% solution in water at 25 °C |
| Surface Tension | 24 dynes/cm = 0.024 N/m at 20 °C |
| Ionization Potential | 10.13 eV |
| Polymerization | Violent polymerization reaction on contact with strong acid, strong base, weak acid conditions (e.g., nitrous fumes, sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide), thiourea, or dimethylamine. |
| Odor Threshold | Odor Threshold Low: 0.02 [mmHg] Odor Threshold High: 1.8 [mmHg] Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 1.8 ppm) Odor threshold = between 0.02 and 0.4 |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.4017 at 20 °C/D |
| Kovats Retention Index | 462 470 469 463 463 463 464 469 465 467.7 473.1 453.7 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Conversion factors: 1 mg/l = 437 ppm; 1 ppm = 2.3 mg/cu m |
| Chemical Classes | Toxic Gases & Vapors -> Other Toxic Gases & Vapors |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 56.06 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 56.026214747 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 56.026214747 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 17.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 30.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Acrolein is a colorless or yellow liquid with a disagreeable odor. It dissolves in water very easily and quickly changes to a vapor when heated. It also burns easily. Small amounts of acrolein can be formed and can enter the air when trees, tobacco, other plants, gasoline, and oil are burned. Acrolein is used as a pesticide to control algae, weeds, bacteria, and mollusks. It is also used to make other chemicals.