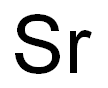CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Other Solid |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Silvery white metal; face-centered cubic structure |
| Boiling Point | 1390 °C |
| Melting Point | 752 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol and acids. |
| Density | 2.54 g/cu cm |
| Vapor Pressure | 4.99X10-11 Pa at 400 K; 0.000429 Pa at 600 K; 1.134 Pa at 800 K; 121 Pa at 1000 K |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Rapidly becomes yellow on exposure to air and assumes an oxide film. |
| Other Experimental Properties | Natural strontium is a mixture of four isotopes; 32 other unstable isotopes are known to exist. Three allotropic forms exist, with transition points at 235 and 540 °C. |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Elements, Metallic |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H260:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H315:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 87.62 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 87.90561225 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 87.90561225 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 1 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Strontium is a naturally occurring element found in rocks, soil, dust, coal, and oil. Naturally occurring strontium is not radioactive and is either referred to as stable strontium or strontium. Strontium in the environment exists in four stable isotopes,84Sr (read as strontium eighty-four),86Sr,87Sr,88Sr. Strontium compounds are used in making ceramics and glass products, pyrotechnics, paint pigments, fluorescent lights, and medicines. Strontium can also exist as several radioactive isotopes; the most common is90Sr.90Sr is formed in nuclear reactors or during the explosion of nuclear weapons. Radioactive strontium generates beta particles as it decays. One of the radioactive properties of strontium is half-life, or the time it takes for half of the isotope to give off its radiation and change into another substance. The half-life of90Sr is 29 years.