57-14-7
Product Name:
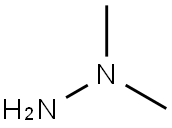
1,1-Dimethylhydrazine
Formula:
C2H8N2
Synonyms:
asym-Dimethylhydrazine;1,1-Dimethylhydrazine
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | 1,1-dimethylhydrazine appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Flash point 0 °F. Corrosive to the skin. Less dense than water and soluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air and very toxic by inhalation, attacking the eyes and respiratory system. Prolonged exposure of containers to heat may result in their violent rupturing and rocketing due to decomposition. Generates toxic oxides of nitrogen when burned. Vapors may travel to a source of ignition and a flame can flashback to the source of vapors. Used as a rocket propellant and to make other chemicals. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | CLEAR, COLORLESS LIQUID |
| Odor | Characteristic ammonia like fishy odor of aliphatic hydrazines |
| Boiling Point | 147 °F at 760 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Melting Point | -72 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Flash Point | 5 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | Decomposes (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 0.7914 at 71.6 °F (EPA, 1998) - Less dense than water; will float |
| Vapor Density | 1.94 (EPA, 1998) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 157 mmHg at 77 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP | log Kow = -1.19 /Estimated/ |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant = 1.3X10-5 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C /Estimated/ |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Solution stored in dark and cold are relatively stable in absence of oxidants |
| Autoignition Temperature | 480 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomp it emits highly toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/. |
| Viscosity | 0.492 millipascal second @ 25 °C |
| Corrosivity | Highly corrosive. |
| Heat of Combustion | -1979 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 32.623 kJ/mol |
| pH | STRONGLY ALKALINE LIQ |
| Surface Tension | 24.09 dynes/cm at 25 °C |
| Ionization Potential | 8.05 eV |
| Odor Threshold | Odor Threshold Low: 6.1 [mmHg] Odor Threshold High: 14.0 [mmHg] Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 9.2) |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.40753 @ 22.3 °C/D |
| Dissociation Constants | pKa= 7.21 at 25 °C |
| Kovats Retention Index | 527 |
| Other Experimental Properties | CONVERSION FACTORS: 1 MG/L= 4.07 PPM AND 1 PPM= 2.5 MG/CU M |
| Chemical Classes | Nitrogen Compounds -> Hydrazines |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H350:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 60.10 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -0.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 60.068748264 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 60.068748264 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 11.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
1,1-dimethylhydrazine appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Flash point 0 °F. Corrosive to the skin. Less dense than water and soluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air and very toxic by inhalation, attacking the eyes and respiratory system. Prolonged exposure of containers to heat may result in their violent rupturing and rocketing due to decomposition. Generates toxic oxides of nitrogen when burned. Vapors may travel to a source of ignition and a flame can flashback to the source of vapors. Used as a rocket propellant and to make other chemicals.